Brands
Indications for use
Application areas
Density
Filler base
Lidocaine
Hyaluronic acid concentration
Volume (ml)
Duration of action
Layers of the dermis
Country of origin
Wrinkle fillers
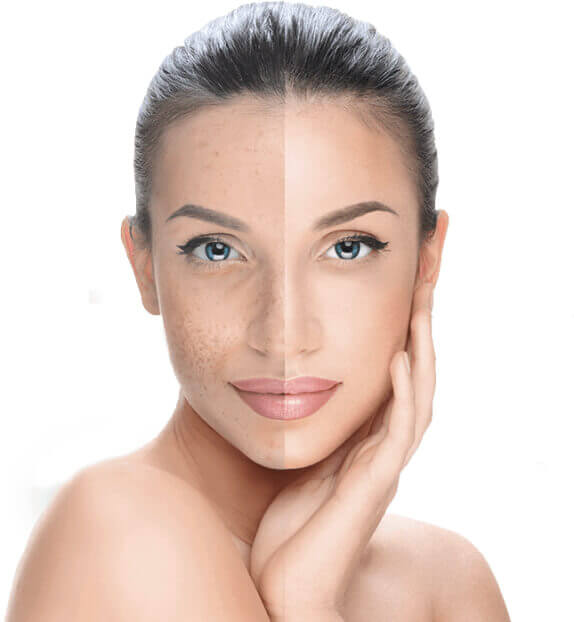
Today it is impossible to imagine cosmetology without injectable fillers and augmentation of the soft tissues of the face and body. The result, which used to be achieved through surgery and long rehabilitation, is now available in one visit to a cosmetologist. And it's all thanks to fillers.
A filler is a gel-like substance that is used for injectable contouring in cosmetology. On the one hand, the beautician injects a wrinkle filler (filling the crease from the inside with a gel-like substance), on the other hand, with a synthetic implant you can give a beautiful volume to the tissues in places where it is necessary.
Filler-type preparations are used for:
● correction of age-related changes (wrinkle filling),
● starting bioprocesses of rejuvenation (neocollagenesis, synthesis of elastin fibers),
● removal of aesthetic imperfections,
● harmonization of facial features.
In cosmetology, fillers are used for contouring not only on the face, but also on the body ( hands, buttocks, neck, decollete area).
What is the history of fillers?
The first attempts of contour plastics were recorded at the end of the XIX century. Then, in Austria and Germany, doctors tried to recreate the shape of male testicles with vaseline oil and restore facial defects with small fragments of the patient's fat.
But the classic use of fillers began in 1902, when Dr. Eckstein tried to use paraffin to fill wrinkles, correct the shape of the nose, cheekbones and increase breasts. The method had some success, and contour plastics began its development.
Which filler was the first?
Only in 1981 the American Association FDA officially approved the first soft tissue filler. It was called Zyderm and was based on collagen.
Which types of fillers are there?
Fillers are broadly classified according to different criteria.
First of all, the preparations are divided into
● Permanent (based on acrylic, silicone, polyacrylamide and so on),
● Biodegradable.
Modern cosmetology has almost completely abandoned the use of a permanent synthetic implant, choosing a biodegradable wrinkle filler.
In turn, biodegradable fillers can be:
● of animal origin (e.g. a filler based on bovine or porcine collagen),
● of non-animal origin (based on synthesized acids and bone tissue elements).
Fillers of non-animal origin have an advantage because they are apirogenic, native, and the risk of a negative immune response and side effects is much lower than when working with preparations of animal origin.
Popular biodegradable fillers have different bases:
● fillers based on hyaluronic acid - HA,
● fillers based on calcium hydroxyapatite - CaHA,
● fillers based on polylactic acid - PLA.
All 3 active substances are native (biocompatible) with our tissues, so they are perfectly accepted by the body and are not rejected.
Classification of fillers based on hyaluronic acid
The most popular on the market are fillers based on hyaluronic acid. Their distinctive feature is the ability of hyularonate molecules to attract and retain water molecules. Thus, a volume is created that fills the tissue deficit from the inside, and the most important regenerative processes are launched in the cells.
Fillers based on HA are divided into:
● Monophasic (contain molecules of the same size),
● Biphasic (contain molecules of different sizes).
Each of these types is used for its own purpose and has both advantages and disadvantages.
Differences between fillers based on CaHA and PLA and hyaluronic fillers
Unlike fillers based on HA that simply fill wrinkles and activate cellular processes, calcium hydroxyapatite and polylactic acid are collagen stimulants. These fillers activate the formation of new collagen fibers in the dermis, which continue to maintain turgor like an elastic skeleton after the breakdown of the filler.
These fillers are much denser and have different rheological properties, so they cannot be implanted in delicate areas: around eyes, tear troughs, forehead or neck.
Before you buy a filler based on these components, it is important to consider one peculiarity:
● Fillers based on hyaluronic acid can be neutralized with hyaluronidase injections in case of an unsuccessful correction,
● Fillers based on CaHA and PLA cannot be dissolved.